Discover effective treatment options for hyperpigmentation, from face acids and retinoids to laser therapy and lightening creams.
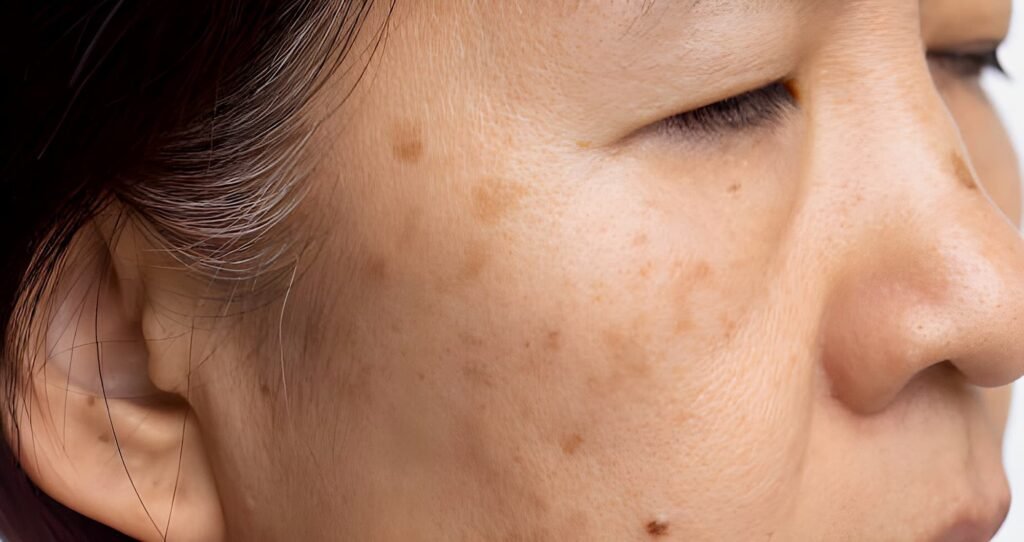
Hyperpigmentation isn’t a specific condition but rather a term used to describe skin that appears darker. It can:
While increased pigmentation is usually not harmful, it can indicate an underlying medical issue. Here’s more information on the types of hyperpigmentation, their causes, and treatment options.
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, with the most common being melasma, sunspots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
The primary symptom of hyperpigmentation is darkened patches of skin. These patches can vary in size and may appear anywhere on the body.
The most significant risk factors for general hyperpigmentation are sun exposure and inflammation, as both can stimulate melanin production. The more sun exposure you have, the greater your risk of developing increased skin pigmentation.
Depending on the specific type of hyperpigmentation disorder, other risk factors may include:
A common cause of hyperpigmentation is the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin is produced by skin cells known as melanocytes. Several conditions or factors can disrupt melanin production in the body.
Certain medications can lead to hyperpigmentation, and some chemotherapy drugs may cause it as a side effect.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also affect melanin production in some women.
A rare endocrine disorder called Addison’s disease can result in hyperpigmentation, which is especially noticeable in areas exposed to the sun (such as the face, neck, and hands) and areas subject to friction (such as the elbows and knees).
Increased melanin synthesis in these cases is directly linked to higher levels of a hormone in the body.
Excessive sun exposure can also lead to increased melanin production.
A dermatologist can identify the cause of your hyperpigmentation by reviewing your medical history and performing a physical examination. In certain instances, a skin biopsy might be conducted to pinpoint the exact cause.
Prescription creams are effective in managing some forms of hyperpigmentation. These treatments often include hydroquinone, a substance that helps to lighten the skin.
However, continuous use of hydroquinone without breaks can result in a condition called ochronosis, where the skin may darken instead. Therefore, it’s essential to use hydroquinone under the supervision of a dermatologist who can guide its proper use to avoid any negative effects.
Topical retinoids are another option that can help diminish dark spots.
It’s important to note that both treatments can take several months before noticeable results appear.
An essential part of managing hyperpigmentation is incorporating sunscreen into your daily routine. Sunscreen plays a vital role in addressing most forms of hyperpigmentation. Consider these features when choosing a sunscreen:
Apply sunscreen every day. If you’re outdoors, reapply every two hours, or more frequently if you’re sweating or swimming.
For conditions like melasma, which can be influenced by visible light, a mineral sunscreen with iron oxide is advisable to help block this light. Additionally, wearing SPF-infused, sun-protective clothing can further protect your skin.
Your dermatologist might also recommend treatments such as laser therapy or chemical peels, depending on the underlying cause of the hyperpigmentation.
Preventing hyperpigmentation entirely might not always be feasible, but you can reduce your risk by:
Avoiding certain medications might also help minimize the likelihood of developing hyperpigmentation.
Generally, hyperpigmentation is not dangerous and doesn’t indicate a severe health issue. In many situations, dark patches may gradually fade with consistent sun protection. However, in some cases, more intensive treatment may be necessary. Even with treatment, there’s no absolute guarantee that dark spots will completely disappear.